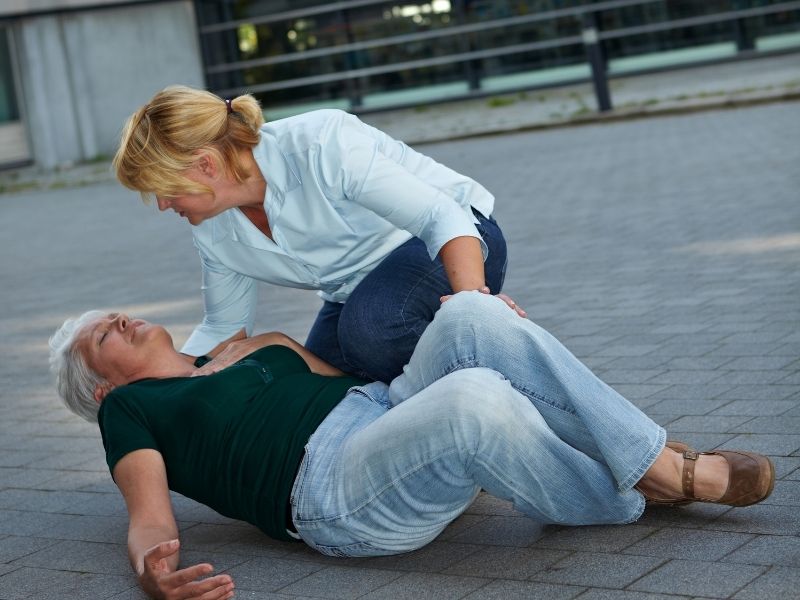
A seizure is an uncontrollable electrical disruption in the brain that occurs suddenly. It can alter the attitude, emotions, or sensations, as well as the degree of awareness. A strong seizure is marked by violent shaking and a lack of control. Seizures aren’t all the same. A seizure might occur as a single occurrence as a result of an immediate reason, such as medicine. Epilepsy is a condition in which a person experiences recurrent seizures. Seizures come in a variety of forms, each with its own set of symptoms and intensity. Although medicine may manage most seizure disorders, seizure treatment could still have a substantial influence on the everyday life
Types of Seizures
The International League For Epilepsy has invented different words to define and categorize seizures. It might be difficult to recognize when someone is suffering a seizure. When someone is suffering a seizure, individuals may appear perplexed or as if they are looking at what isn’t there. Patients with surgical treatment may be prime candidates if their seizures are caused by focused scarring or other neurological issues.
Generalized seizures
Seizures with generalized onset are characterized by surges of aberrant nerve discharges that occur in the cortex of the brain at nearly the same time. Simultaneously, these seizures impact both hemispheres of the brain or clusters of neurons on both sides of the brain. Although generalized seizures may have had a hereditary component, only a tiny percentage of persons who experience them encounter family relatives who also have them.
• Absence Seizures: Individuals will blackout or stare towards nowhere for a few moments during an absence seizure. Grand mal seizures are another name for them. Children are the most commonly affected by absence seizures, which usually do not result in long-term complications.
• Tonic and Atonic Seizures: An atonic seizure (also known as a ‘drop attack’) occurs when a person’s body relaxes and then becomes flexible. Tonic seizures are usually quite short and come on suddenly. Tonic seizures produce rapid rigidity in the arms and body in some persons, generally those with severe brain injuries and cognitive disabilities, which can lead to falls and injury.
• Clonic seizures: Clonic seizures occur when the muscles contract, causing the facial, neck, and arm muscles to twitch regularly. They might last a few minutes.

- Focal Seizures: Focal seizures can begin in one section of the brain and extend to other parts, generating moderate to severe consequences based on how much of the brain is affected. The manner a kid behaves throughout a focal seizure is determined by the portion of the brain that is impacted. A focal conscious seizure occurs when the electrical activity of the seizure remains in one sensory or motor region of the brain.
What are the consequences of having a seizure?
There are surges of electrical activity in the brain throughout a seizure, similar to an electrical storm. Based on the sort of seizure and where portion of the brain is engaged, this movement produces a variety of symptoms. Epilepsy come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and they impact people differently. Some people are aware that a seizure might occur hours, days, or perhaps even weeks in advance. Others may be unaware of the onset and are unaware of any warning indications. A “prodrome” is an early warning symptom of a seizure.
The “ictal period” refers to the midst of a seizures. This is the interval between the onset of observable seizure signs including an aura if patients have one and the cessation of seizure events in the brain. Even after the seizure activity in the brain has ended, people may still experience certain sensations.

What methods are used to identify seizures?
Diagnosing seizure patterns might be challenging for physicians. Certain diagnostics may be recommended by the doctor to correctly diagnose a seizure and verify that the therapies they prescribe are successful.
The physician will take into account the whole health information as well as the events leading up to the seizure. Migraine, migraines, sleep difficulties, and acute psychosocial problems, for instance, can all lead to seizure-like episodes.
Other disorders that might induce seizure-like behavior may be ruled out by lab testing. For diagnosis around Huston visit West Huston Internal Medicine by calling to get an appointment at (832)-321-4962
Treatment
Antiepileptic medicines (AEDs), nutrition treatment, and neurosurgery are among the options for treating epilepsy. Medicines are typically always the first line of therapy for people with numerous seizures. If someone or a kid suffers a seizure for the very first time, if there are multiple seizures, or if the seizures occur more frequently than normal, see a specialist.
Medication
Epilepsy patients will almost always require medication to keep their seizures under management. Antiepileptic medicines are the name for these treatments. They work by focusing on the transmission activity of certain brain cells and in around 70% of instances, medicines can successfully control seizures.
Nerve stimulation
A pacemaker-like device is implanted into the chest for nerve stimulation. These gadgets then provide electrical impulses to the nerve, which can help manage seizures.
Surgery
If drugs do not help, physicians may suggest surgical methods to manage epilepsy and seizures. Surgery to eliminate the brain tissue that is the source of seizures may be explored for seizure activities that are unresponsive to previous therapies.
Ketogenic diet
Dietary adjustments may aid in the lengthy management of epilepsy and seizure incidence reduction. A specific diet known as the ketogenic diet may assist certain forms of seizures in children who do not respond to medicines.






0 Comments